-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
v0.4.0 Lab 3 Deploy Dependencies
In order to successfully deploy and test all modules in your desired environment some modules have to have resources deployed beforehand. In this lab you will deploy the modules' dependencies by manually triggering the dependency pipeline.
- Step 1 - Add a dependency resource parameter
- Step 2 - Update the dependency workflow
- Step 3 - Upload your changes to GitHub
- Step 4 - Trigger the dependency pipeline
- Step 5 - Understand the dependency pipeline
Dependency resource parameters are hosted by the utilities\pipelines\dependencies subfolder. Under that, the relative path to the dependency resource folder is consistent with its resource type.
Example: The folder hosting key vault resources is
utilities\pipelines\dependencies\Microsoft.KeyVault\vaultssince the key vault resource type isMicrosoft.KeyVault\vaults
As part of a later lab you will need an additional dependency, a proximity placement group, that is currently not part of the dependency pipeline. For this purpose, perform the following tasks to add the new dependency.
-
The resource type of the proximity placement group resource is
Microsoft.Compute\proximityPlacementGroups. In your local VSCode, navigate to the dependencies compute folderutilities\pipelines\dependencies\Microsoft.Compute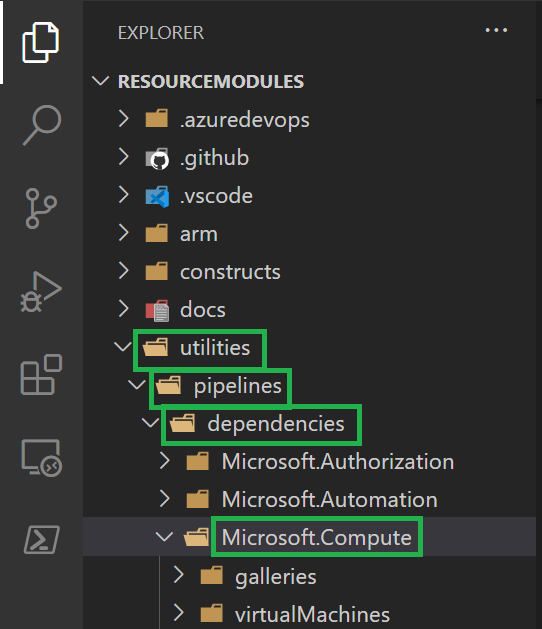
-
Add a new folder
proximityPlacementGroups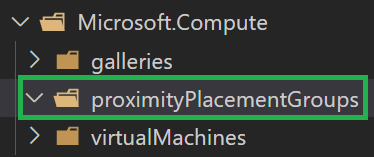
-
Add another nested folder called
parameters. This folder hosts all parameter files you would use to deploy proximity placement group dependencies. -
In the parameters folder, add a new parameter file
parameters.json. This file hosts the minimum parameters you need to deploy the dependency.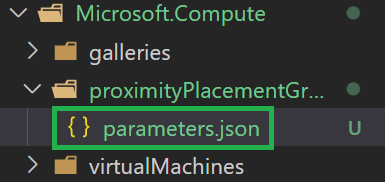
Note: The file's full path should match
utilities\pipelines\dependencies\Microsoft.Compute\proximityPlacementGroups\parameters\parameters.json. -
Add the below snippet to the file
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentParameters.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "name": { "value": "adp-<<namePrefix>>-az-ppg-x-001" } } }
Together with the resource modules pipelines, we are providing a dependency pipeline (GitHub workflow: .github\workflows\platform.dependencies.yml), leveraging resource parameters from the utilities\pipelines\dependencies subfolder.
Note: If this was a contribution to the main CARML repository, we would ask you to perform the same update to the Azure DevOps dependency pipeline
-
Navigate to the dependency pipeline in path
.github\workflows\platform.dependencies.yml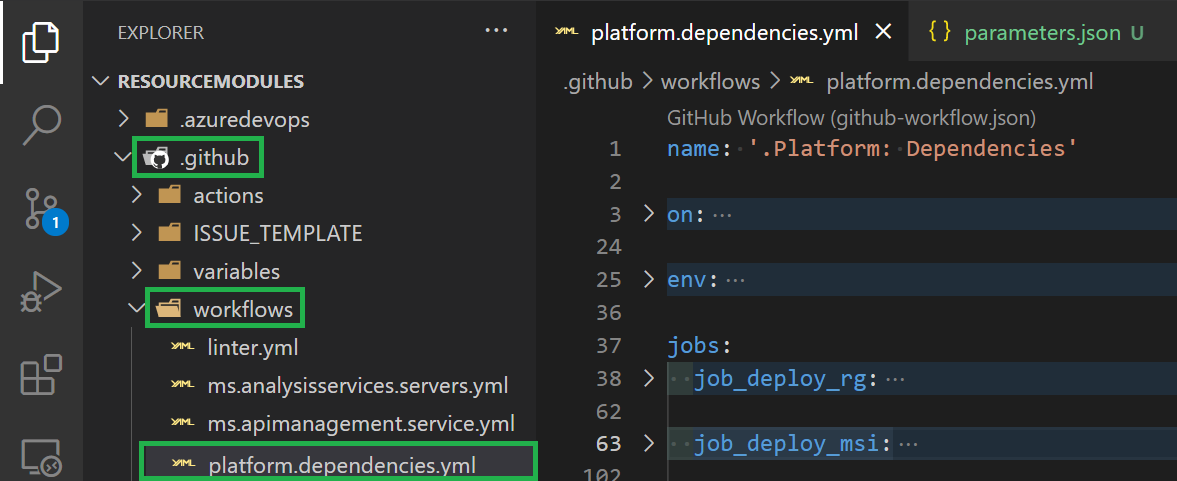
-
Add the below snippet in between the
job_deploy_rg&job_deploy_msijob in line 62. You can add spaces as you see fit.Note: YAML is space-sensitive. Make sure the snippet uses the same indent as the other jobs.
job_deploy_ppg: runs-on: ubuntu-20.04 name: 'Deploy proximity placement group' env: namespace: 'Microsoft.Compute\proximityPlacementGroups' needs: - job_deploy_rg strategy: fail-fast: false matrix: parameterFilePaths: ['parameters.json'] steps: - name: 'Checkout' uses: actions/checkout@v2 with: fetch-depth: 0 - name: 'Deploy module' uses: ./.github/actions/templates/validateModuleDeployment with: templateFilePath: 'arm/${{ env.namespace }}/deploy.bicep' parameterFilePath: '${{ env.dependencyPath }}/${{ env.namespace }}/parameters/${{ matrix.parameterFilePaths }}' location: '${{ env.defaultLocation }}' resourceGroupName: '${{ env.defaultResourceGroupName }}' subscriptionId: '${{ secrets.ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }}' managementGroupId: '${{ secrets.ARM_MGMTGROUP_ID }}' removeDeployment: '${{ env.removeDeployment }}'
Now that the new dependency is implemented, you can upload your changes to GitHub.
This can either be done via the terminal or by using the Git integration of VSCode:
Alternative 1: Via VSCode's terminal
-
If a Terminal is not in sight, you can alternatively open it by expanding the
Terminal-dropdown on the top, and selectingNew Terminal -
Now, execute the following PowerShell commands:
git add . git commit -m 'Added Proximity Placement Group to dependency pipeline' git push
Alternative 2: Via VSCode's UI
-
Add your changes: If not already there, navigate to the source control menu to the left and add the changed files to the commit. To do so, select the
+icon next toChanges(appears when hovering)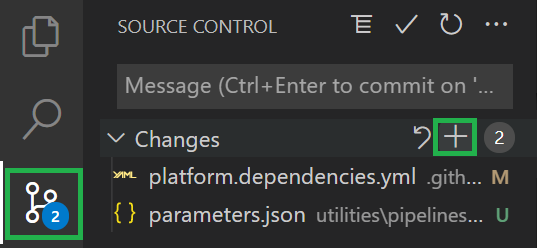
-
Commit your changes: Next, you should give the commit a meaningful message such as 'Added Proximity Placement Group to dependency pipeline' and can then click the checkmark symbol on the top to create the commit
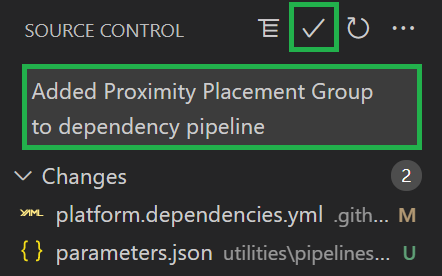
-
Push your changes: Finally, you can push the changes to the repository by selecting the blue
Publish Branchbutton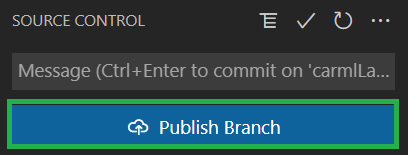
Usually, the dependency workflow would not run frequently, but only when new module dependencies are identified or its original state must be recovered. Therefore, the type of trigger that has been configured is the workflow_dispatch, which allows us to manually trigger the workflow when needed.
-
In the repository menu open the
Actionstab.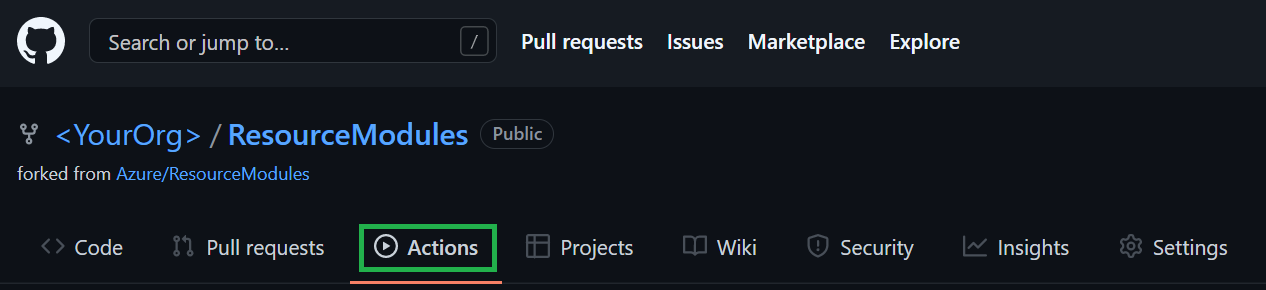
-
From the workflows list, select the one named
.Platform: Dependencies.
-
To the right, you will see a
Run workflowbutton. Click on it, select your branch from the branch dropdown menu and trigger the workflow by clicking on the green buttonRun workflow.
For the sake of saving time in the lab, we will leave the SQL Managed Identity and VHD check boxes unchecked.
-
After running the workflow, if you wait a few seconds or refresh the page, you will see that a new execution is in progress.

-
You will verify that the workflow has finished once the status is green.
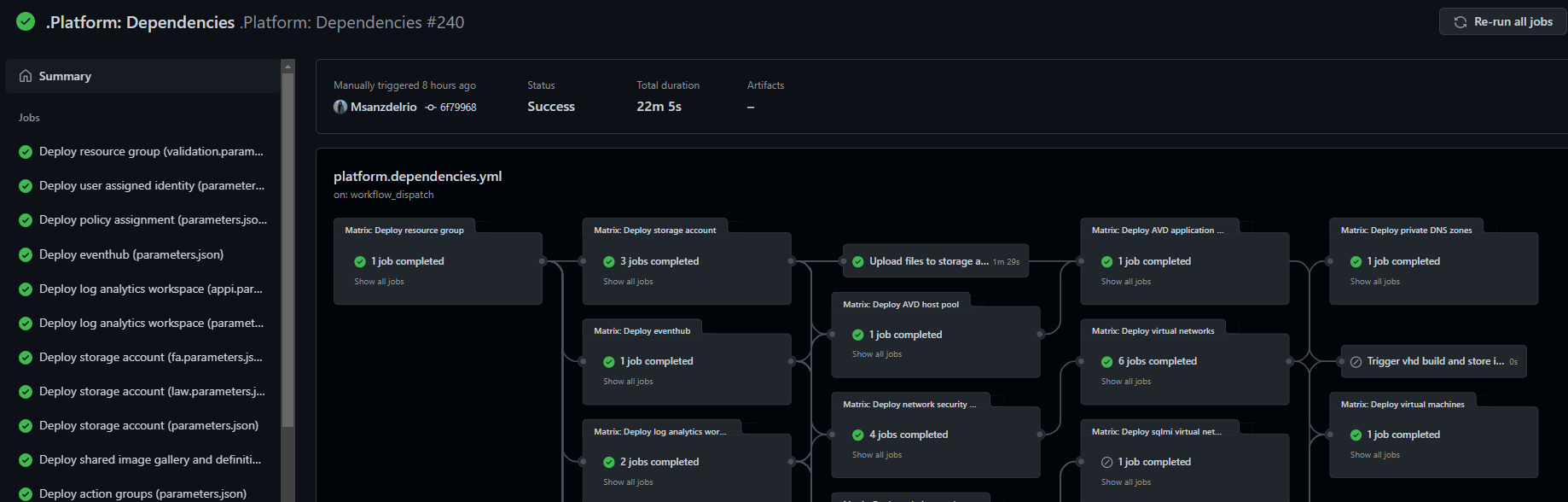
This workflow may take up to 30 minutes to execute. You can proceed with the following steps and labs and revisit the pipeline later to make sure it succeeded.
In order to successfully deploy and test all modules in your desired environment some modules have to have resources deployed beforehand. Since also dependency resources are in turn subject to dependencies with each other, resources are deployed in the following grouped order.
First level resources: resource groups leveraged by all modules. One instance is deployed:
-
validation-rg: The resource group to which resources are deployed by default during the test deployment phase. This same resource group is also the one hosting the dependencies.
Second level resources: This group of resources has a dependency only on the resource group which will host them. Resources in this category include a log analytics workspace, storage account, event hub namespace, etc.
Note: This group contains the previously added Proximity Placement group
Third level resources: This group of resources has a dependency on one or more resources in the group above. In this group we can find a key vault, recovery services vault, application insights, etc.
Fourth level resources: This group of resources has a dependency on one or more resources in the groups above. These resources include some virtual networks and a AVD application group.
Finally, the fifth level resources are resources with dependency on all the other groups. They include a virtual machine and a private DNS zone.

If ready, proceed to the next lab: Lab 4 - First pipeline run
This wiki is being actively developed