SalCrop: Spatio-temporal Saliency Based Video Cropping
Related Project
- Kao Zhang, Zhenzhong Chen. Video Saliency Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Two-Stream Network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 3544-3557, 2019.
Github: https://github.com/zhangkao/IIP_TwoS_Saliency
Video cropping is a key research task in video processing field. In this paper, a spatio-temporal saliency based video cropping framework (SalCrop) is introduced including four core modules: video scene detection module, video saliency prediction module, adaptive cropping module, and video codec module. It can automatically reframe videos in the desired aspect ratios. In addition, a large-scale video cropping dataset (VCD) is built for training and testing. Experiments on the VCD test dataset show that our SalCrop outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithms with high efficiency. Besides, a FFmpeg video filter is developed based on the framework, which can be widely used in different scenarios. A demo is available at: https://mme.tencent.com/smartcontent/videoCrop (access token: test_token).
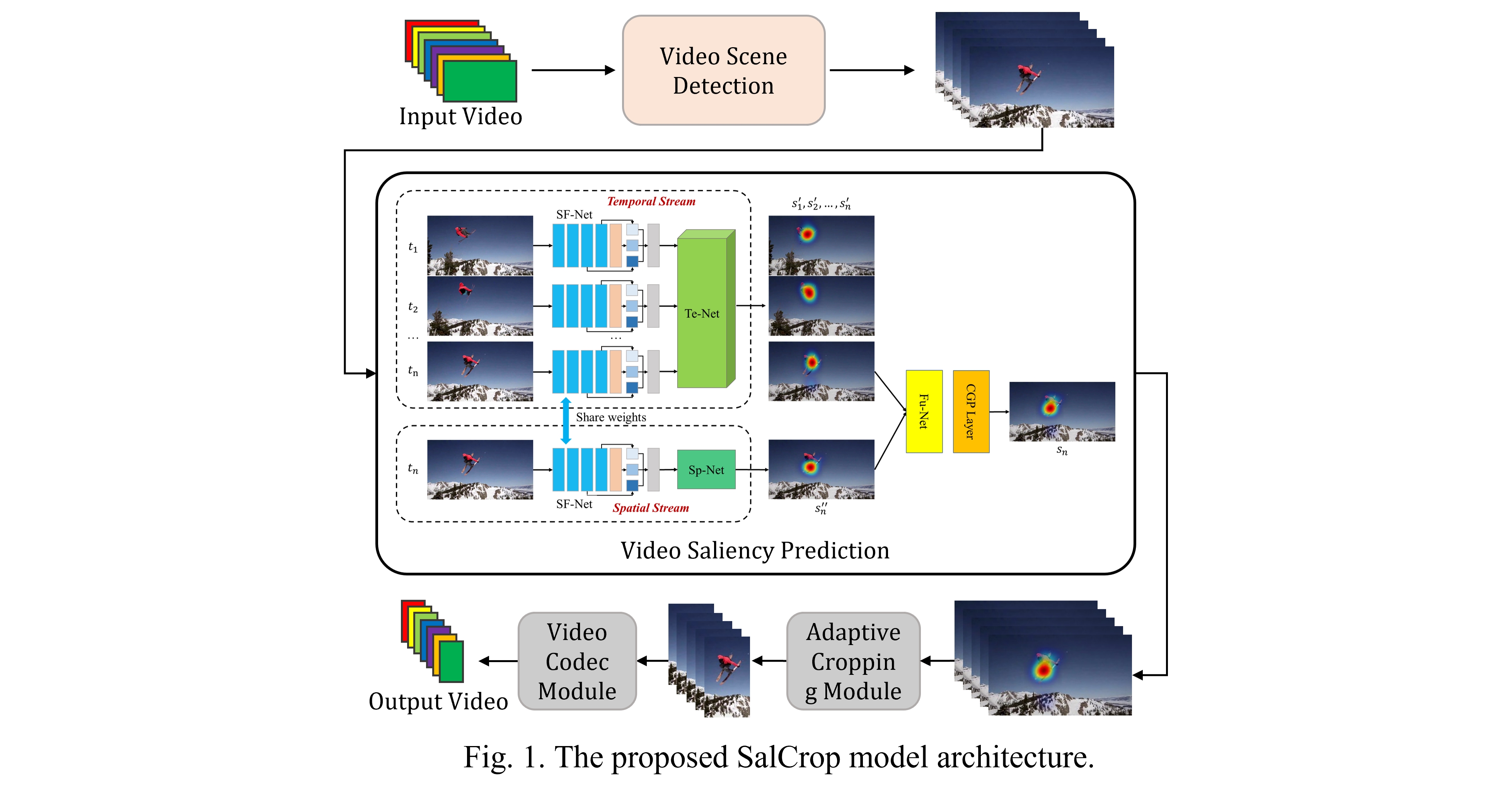
The framework of SalCrop is shown in Figure 1 It contains four main modules:
- Video Scene Detection module, in which long videos are automatically split into short sequences with consecutive shots based on key frames;
- Video Saliency Prediction module, in which a lightweight two-stream network is proposed to find salient content in the frames;
- Adaptive Cropping module, which can automatically choose an optimal cropping strategy to reframe videos with continuous and steady viewpoint, depending on the distribution of salient targets/regions in different frames;
- Video Codec module for video encoding and decoding.
A large-scale video cropping dataset (VCD) is proposed, which consists of 300 videos with various categories and photographic styles selected from three public video saliency prediction datasets: LEDOV, AVS1K, and DIEM. There are five subsets, including 60 clips of animals, 100 clips of man-made objects, 110 clips of human beings, 10 clips of landscapes, and 20 clips of others. These videos vary in the number of frames and resolution. The dataset is divided into three parts randomly: 200 sequences for training, 50 sequences for validation and 50 sequences for testing. Example frames from VCD are shown in Figure 2.
Dataset examples: List of all videos (6K) List of test videos (0.7K) VCD data example (530M)
Our SalCrop is implemented in Python 3.7 and Pytorch 1.5 environment with a single NVIDIA V100 GPU and 2.5 GHz Intel Xeon Platinum 8255C CPU.
We conduct subjective assessment experiments on the VCD test dataset with 21 participants to compare our SalCrop with two state-of-the-art video cropping methods: Google AutoFlip and Adobe AutoReframe. Different from video quality assessment, the subjective perception evaluation focuses on two main factors: content integrity and temporal consistency. A higher score should be assigned to the video that can fully express the main information of the original video, while the content is continuous and smooth in temporal dimension. Five-level scale is used for evaluation, in which numbers 1 to 5 are used to indicate the quality from bad to excellent. The cropped videos of these three methods are randomly shuffled and rated by the subjects. The comparison results are shown in Figure 3. Our SalCrop achieves better performance (3.9) than AutoFlip (2.6) and AutoReframe (3.4) with ultra-fast speed (about 200FPS ignoring IO cost). In addition, the combination of sampling and interpolation operations can be used to further improve efficiency.
Result examples: SalCrop (113M),
Taking a video and a target aspect ratio (default 9:16 for the demo) as inputs, SalCrop can automatically analyze the video content, develop an optimal cropping strategy, and generate a reframed output video. A demo is available at: https://mme.tencent.com/smartcontent/videoCrop (access token: test_token). More demo videos can be found at YouTube or OneDrive (470M).
The first phase of this work was supported in part by Tencent.
The second phase of this work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 62201404 and No. 62036005, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under contract No. 2021M692463, Postdoctoral Innovative Research Position Funding of Hubei Province of China, LIESMARS Special Research Funding, and Tencent.
If you use the UAVSal video saliency model, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{zhang2022SalCrop,
title={SalCrop: Spatio-temporal Saliency Based Video Cropping},
author={Zhang, Kao and Yan, Shang and Li, Songnan and Liu, shan and Chen, Zhenzhong},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP) demo paper},
year={2022}
}
Kao Zhang and Yan Shang are co-first authors.
Kao ZHANG
Laboratory of Intelligent Information Processing (LabIIP)
Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
Email: zhangkao@whu.edu.cn
Zhenzhong CHEN (Professor and Director)
Laboratory of Intelligent Information Processing (LabIIP)
Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
Email: zzchen@whu.edu.cn
Web: http://iip.whu.edu.cn/~zzchen/