This project is my own implementation of the K-means algorithm from scratch, using only Python and NumPy based on a previous version I did in the AI - LSIA class, now making a model with different datasets.
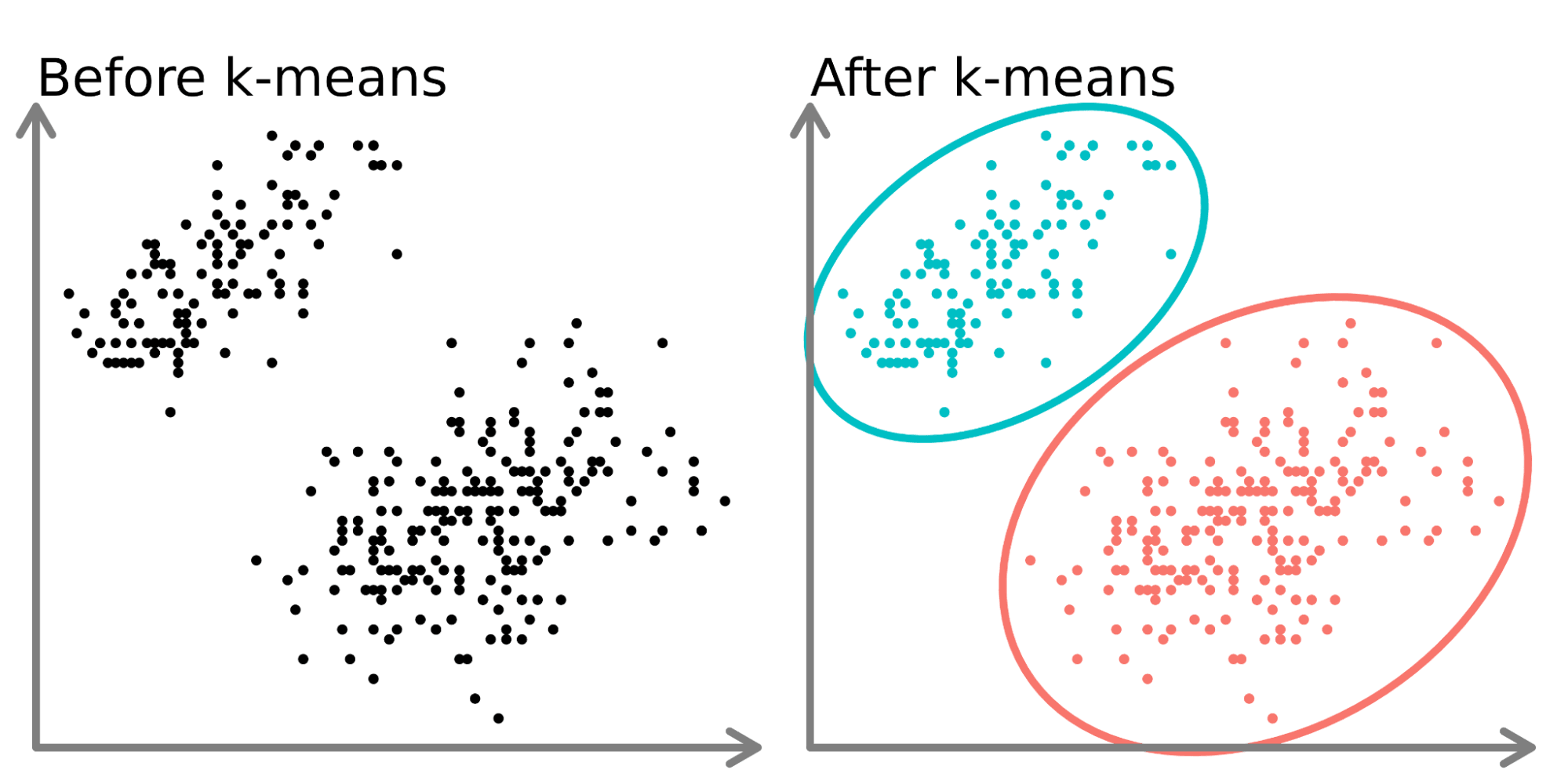
K-means clustering is an unsupervised learning algorithm used for data clustering , which groups unlabelled data points into groups or clusters.
While there are several types of clustering algorithms, including exclusive, overlapping, hierarchical and probabilistic, the k-means clustering algorithm is an example of an exclusive or "hard" clustering method.
This form of clustering stipulates that a data point can exist in only one cluster. This type of cluster analysis is commonly used in data science for market segmentation, document clustering, image segmentation and image compression. The k-means algorithm is a widely used method in cluster analysis because it is efficient, effective and simple.
K-means is a centroid-based iterative clustering algorithm that divides a dataset into similar groups based on the distance between their centroids. The centroid, or centre of the cluster, is the mean or median of all points within the cluster, depending on the characteristics of the data.
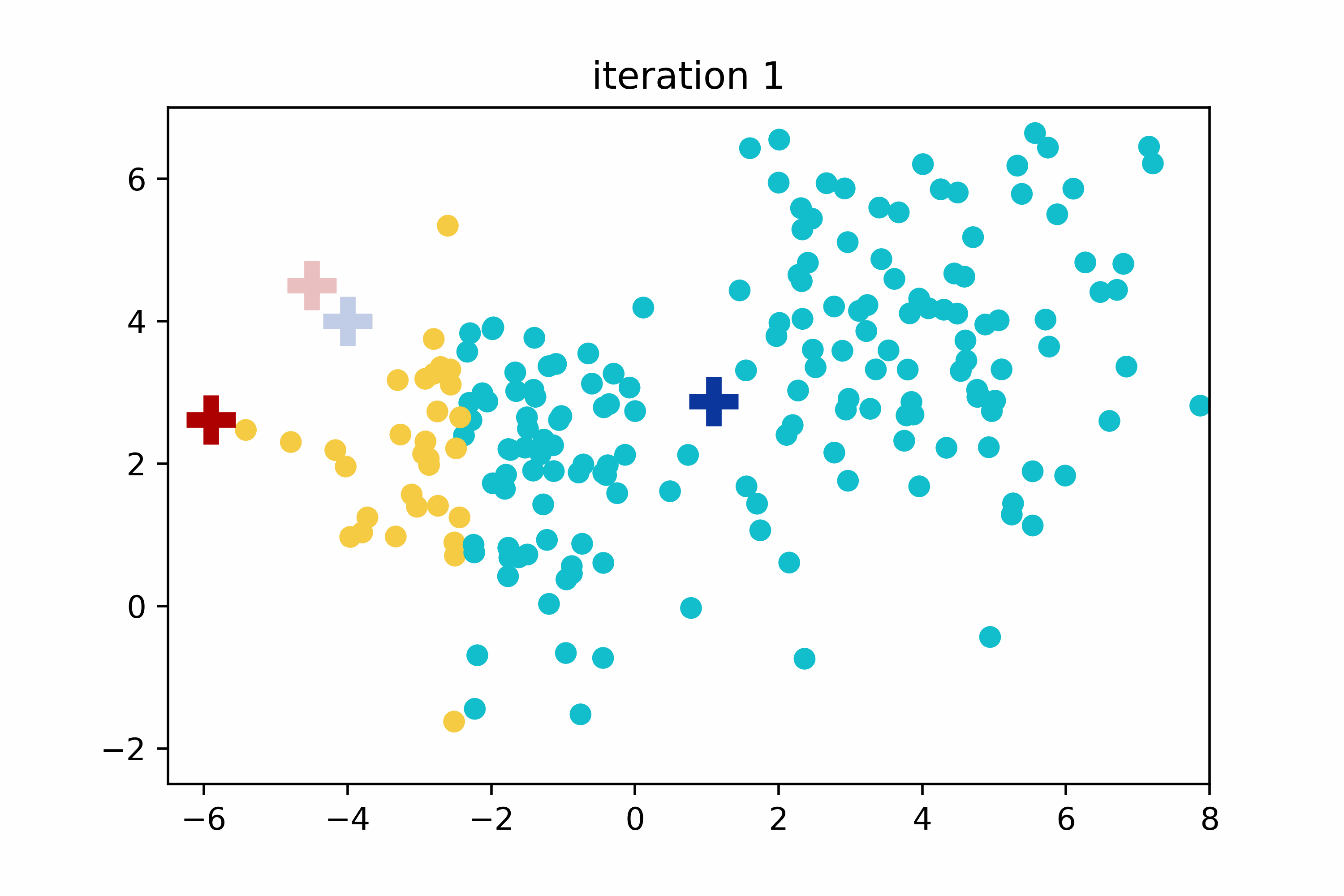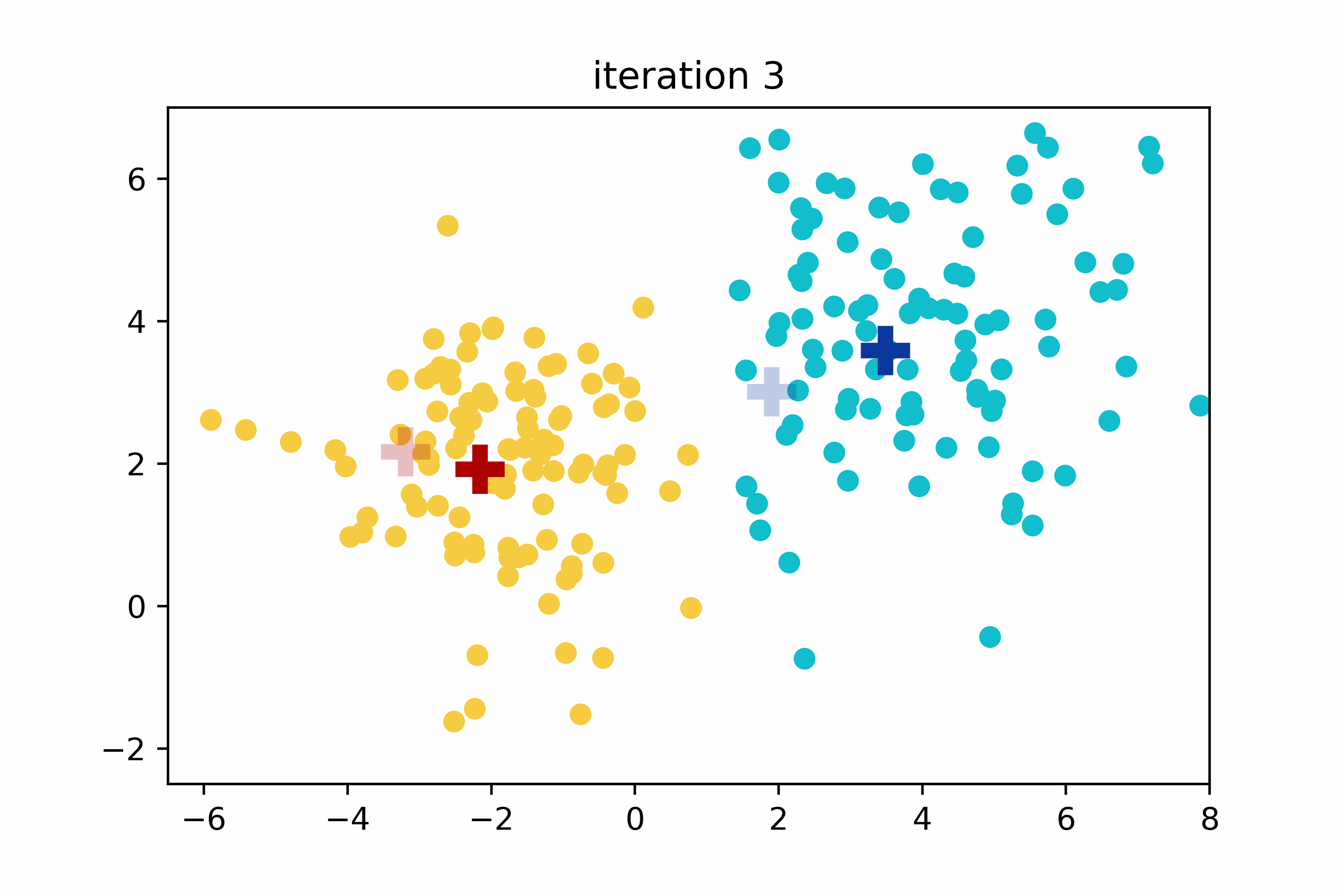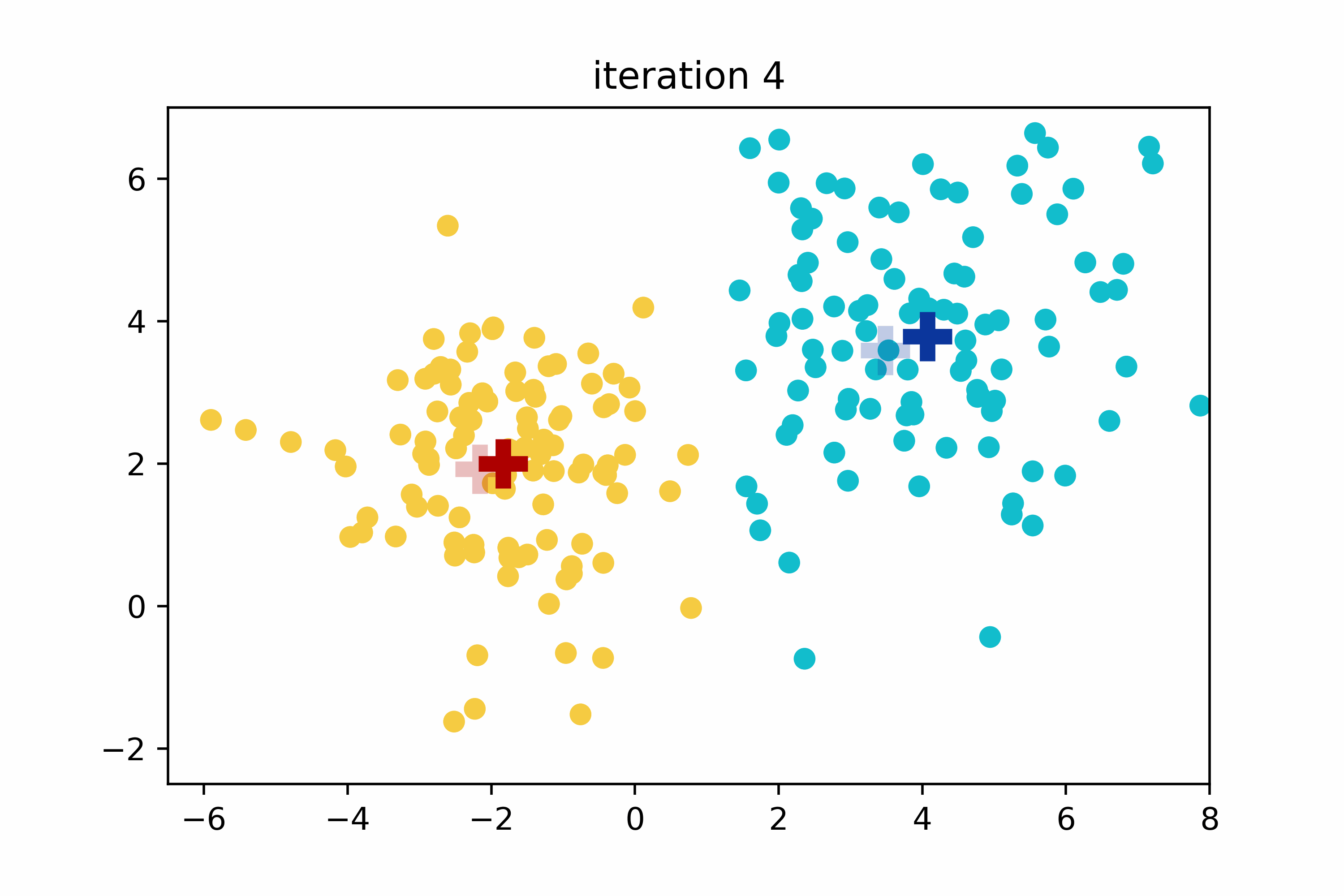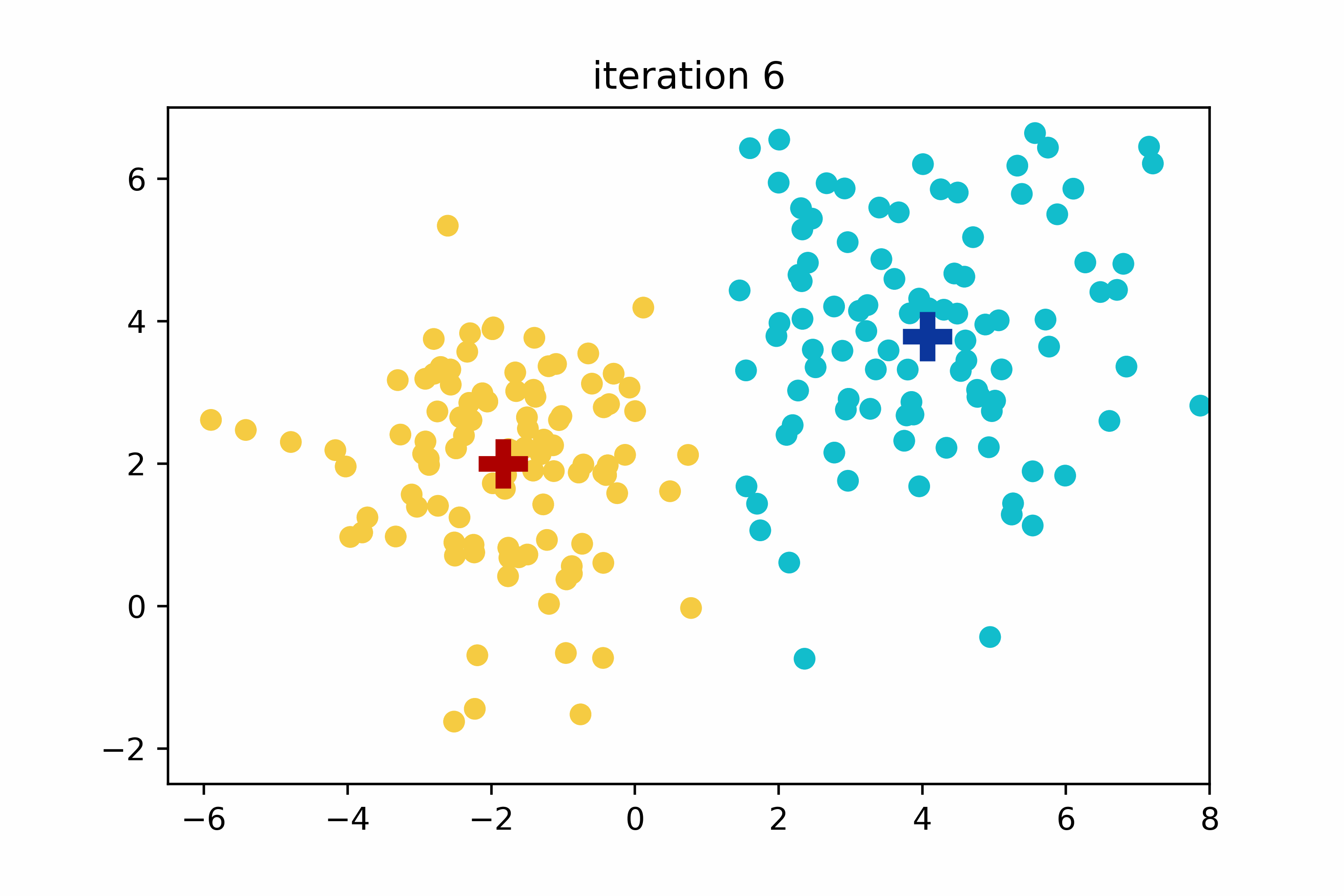
1. Initialise K random centroids.
2. Repeat until convergence or a maximum number of iterations:
a. For each data point in the data set:
i. Assign the data point to the nearest centroid.
b. For each cluster:
i. Update the centroid by calculating the mean of the points assigned to the cluster.
3. End
The K-means algorithm is not deterministic due to its random initialization step. This means that if the algorithm is run twice with identical data, the group assignments may differ. To achieve optimal clustering results, the proper selection of initial centroids and the determination of the optimal number of clusters improve both the accuracy and the speed of the K-means algorithm.
-
Customer Segmentation: The practice of dividing a company’s customers into groups based on shared characteristics that reflect similarities. This strategy allows companies to target specific customer groups with tailored advertising campaigns.
-
Document Classification: A process of assigning various classes or categories to documents. Many organizations use this method to moderate content. Refer to Watson Discover’s documentation to create a document classifier.
-
Image Segmentation: A computer vision technique that divides a digital image into distinct sets of pixels. This research delves into how K-means models are used to help identify boundaries in medical images.
-
Recommendation Engines: Applications across the web use recommendation engines. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering techniques are employed to generate product recommendations for e-commerce businesses.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to implement | Must manually chose K |
| Always converges to local minimum | Not guaranteed to find global minimum |
| Scales well to large datasets | May not perform well on data of varying density |
| Generalizes to clusters of different shapes and sizes | Clusters are biased by outliers |