sdcat
Sliced Detection and Clustering Analysis Toolkit
This repository processes images using a sliced detection and clustering workflow. If your images look something like the image below, and you want to detect objects in the images, and optionally cluster the detections, then this repository may be useful to you. The repository is designed to be run from the command line, and can be run in a Docker container, without or with a GPU (recommended).
Detection can be done with a fine-grained saliency-based detection model, and/or one the following models run with the SAHI algorithm. Both detections algorithms are run by default and combined to produce the final detections.
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| yolov8s | YOLOv8s model from Ultralytics |
| hustvl/yolos-small | YOLOS model a Vision Transformer (ViT) |
| hustvl/yolos-tiny | YOLOS model a Vision Transformer (ViT) |
| MBARI-org/megamidwater (default) | MBARI midwater YOLOv5x for general detection in midwater images |
| MBARI-org/uav-yolov5 | MBARI UAV YOLOv5x for general detection in UAV images |
| MBARI-org/yolov5x6-uavs-oneclass | MBARI UAV YOLOv5x for general detection in UAV images single class |
| FathomNet/MBARI-315k-yolov5 | MBARI YOLOv5x for general detection in benthic images |
To skip saliency detection, use the --skip-saliency option.
sdcat detect --skip-saliency --image-dir <image-dir> --save-dir <save-dir> --model <model> --slice-size-width 900 --slice-size-height 900To skip using the SAHI algorithm, use --skip-sahi.
sdcat detect --skip-sahi --image-dir <image-dir> --save-dir <save-dir> --model <model> --slice-size-width 900 --slice-size-height 900Once the detections are generated, the detections can be clustered. Alternatively, detections can be clustered from a collection of images by providing the detections in a folder with the roi option.
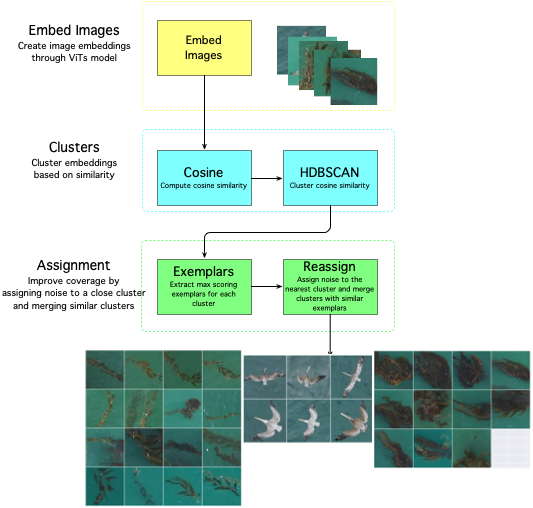
sdcat cluster roi --roi <roi> --save-dir <save-dir> --model <model> The clustering is done with a Vision Transformer (ViT) model, and a cosine similarity metric with the HDBSCAN algorithm. The ViT model is used to generate embeddings for the detections, and the HDBSCAN algorithm is used to cluster the detections. What is an embedding? An embedding is a vector representation of an object in an image.
The defaults are set to produce fine-grained clusters, but the parameters can be adjusted to produce coarser clusters. The algorithm workflow looks like this:
| Vision Transformer (ViT) Models | Description |
|---|---|
| google/vit-base-patch16-224(default) | 16 block size trained on ImageNet21k with 21k classes |
| facebook/dino-vits8 | trained on ImageNet which contains 1.3 M images with labels from 1000 classes |
| facebook/dino-vits16 | trained on ImageNet which contains 1.3 M images with labels from 1000 classes |
| MBARI-org/mbari-uav-vit-b-16 | MBARI UAV vits16 model trained on 10425 UAV images with labels from 21 classes |
Smaller block_size means more patches and more accurate fine-grained clustering on smaller objects, so ViTS models with 8 block size are recommended for fine-grained clustering on small objects, and 16 is recommended for coarser clustering on larger objects. We recommend running with multiple models to see which model works best for your data, and to experiment with the --min-samples and --min-cluster-size options to get good clustering results.
Pip install the sdcat package with:
pip install sdcatAlternatively, Docker can be used to run the code. A pre-built docker image is available at Docker Hub with the latest version of the code.
Detection
docker run -it -v $(pwd):/data mbari/sdcat detect --image-dir /data/images --save-dir /data/detections --model MBARI-org/uav-yolov5Followed by clustering
docker run -it -v $(pwd):/data mbari/sdcat cluster detections --det-dir /data/detections/ --save-dir /data/detections --model MBARI-org/uav-yolov5A GPU is recommended for clustering and detection. If you don't have a GPU, you can still run the code, but it will be slower. If running on a CPU, multiple cores are recommended and will speed up processing.
docker run -it --gpus all -v $(pwd):/data mbari/sdcat:cuda124 detect --image-dir /data/images --save-dir /data/detections --model MBARI-org/uav-yolov5To get all options available, use the --help option. For example:
sdcat --helpwhich will print out the following:
Usage: sdcat [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Process images from a command line.
Options:
-V, --version Show the version and exit.
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
cluster Cluster detections.
detect Detect objects in images
To get details on a particular command, use the --help option with the command. For example, with the cluster command:
sdcat cluster --help which will print out the following:
Usage: sdcat cluster [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands related to clustering images
Options:
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
detections Cluster detections.
roi Cluster roi.The sdcat toolkit generates data in the following folders. Here, we assume both detection and clustering is stored in the same root folder:
/data/20230504-MBARI/
└── detections
└── hustvl
└── yolos-small # The model used to generate the detections
├── det_raw # The raw detections from the model
│ └── csv
│ ├── DSC01833.csv
│ ├── DSC01859.csv
│ ├── DSC01861.csv
│ └── DSC01922.csv
├── det_filtered # The filtered detections from the model
├── det_filtered_clustered # Clustered detections from the model
├── crops # Crops of the detections
├── dino_vits8...date # The clustering results - one folder per each run of the clustering algorithm
├── dino_vits8..exemplars.csv # Exemplar embeddings - examples with the highest cosine similarity within a cluster
├── dino_vits8..detections.csv # The detections with the cluster id
├── stats.txt # Statistics of the detections
└── vizresults # Visualizations of the detections (boxes overlaid on images)
├── DSC01833.jpg
├── DSC01859.jpg
├── DSC01861.jpg
└── DSC01922.jpg
The YOLOv8s model is not as accurate as other models, but is fast and good for detecting larger objects in images, and good for experiments and quick results. Slice size is the size of the detection window. The default is to allow the SAHI algorithm to determine the slice size; a smaller slice size will take longer to process.
sdcat detect --image-dir <image-dir> --save-dir <save-dir> --model yolov8s --slice-size-width 900 --slice-size-height 900Cluster the detections from the YOLOv8s model. The detections are clustered using cosine similarity and embedding
features from the default Vision Transformer (ViT) model google/vit-base-patch16-224
sdcat cluster --det-dir <det-dir>/yolov8s/det_filtered --save-dir <save-dir> --use-vits- https://github.com/obss/sahi SAHI
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2 DINOv2
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.02282.pdf HDBSCAN
- https://github.com/muratkrty/specularity-removal Specularity Removal