Scripts to approximate ELO of a UCI chess engine for different number of nodes.
Note: Throughout this document ELO error means an accuracy with which the ELO is measured.
The script executes cutechess-cli and ordo in interleaved fashion. ordo is executed after each game. And there's a stop criterion based on ELO error. All results are saved.
Engine is tested against another engines with known ELO ratings ± error. (So called gauntlet tournament.)
Each engine directory is named using template elo_error_name. Where error is error (like ±24 ELO). For example,
1292_20_scam
Each folder should contain corresponding executable file. So 1292_20_scam folder contains scam executable file.
In the current version the error part isn't used much. You can use 0 instead of it, if you wish. But all the error values are saved in the resulting file, so it can be helpful in some scenarios.
For convenience the search for executable file is case-insensitive.
If the folder name isn't in the format mentioned above - elo_error_name - it's completely ignored.
You can keep version of the engine in the folder name, but it should be separated by -, , _. For exampe, 1292_20_scan-v0.4-64bit can contain scam-v0.4-64bit, or scam-v0.4, or scan executable file.
All engines should be UCI-compatible. (And be able to run in cutechess-cli.)
The ratings provided in this repo are from CCRL Blitz (2+1). You can replace the engines as you with, but bear in mind that ELO depends on time control and testing hardware. One should try to be consistent here.
Main engine (an engine to test) should be placed in the folder main with an executable file main.
There are some open source engines in engines folder. You can add additional engines. But you need to know their ELO.
play script is the main match simulation script.
slowplay used to play with CPU limited.
run is just a convinience script to avoid passing all the command line arguments.
play nodes approximate-elo scripts searches for engines with more or less the same rating as the parameter provided. For example:
play 500000 2600
starts a match with main engine and another 2400-2800 engines. Match where engines have very different ratings can be slow to converge, because all-wins, all-loses situations.
Notice: Playing against just one engine can be problematic, because the pair can be parly pathological: one engine can exploit concrete weakneses of another engine, while another engine can be unable to exploit weakneses of the former engine. This can lead to huge fluctuations in ELO estimates when switching to other opponents with the same nodes regime.
After each game, ordo is run to calculate ELO and ERROR.
The script can be stopped at any time by ctrl+c. (cutechess-cli sometimes adds an empty uncompelted game in this case, the script tries to remove it.) After stopped, the script can be run again without problems, even with different parameters.
Time control can be changed in the play script file - it's time_control global string variable at the top of the script.
All games are saved in games folder. (Output of cutechess-cli and ordo is saved there too in a log file.)
Ratings per nodes from all simulations are saved in play-results.json file. Along with the error.
See full usage information in the play script file.
I run this script on my own pc with another script slowplay which severly limits CPU usage using systemd-run. So time control is changed appropriately (multiplied).
See full usage information in the slowplay script file.
It's just launcher for slowplay to avoid mistakes in arguments.
Also you can batch slowplay tournaments just making several lines in the run script.
Run with
pytohn curve-fit.py
Requires numpy, scipy and matplotlib python modules.
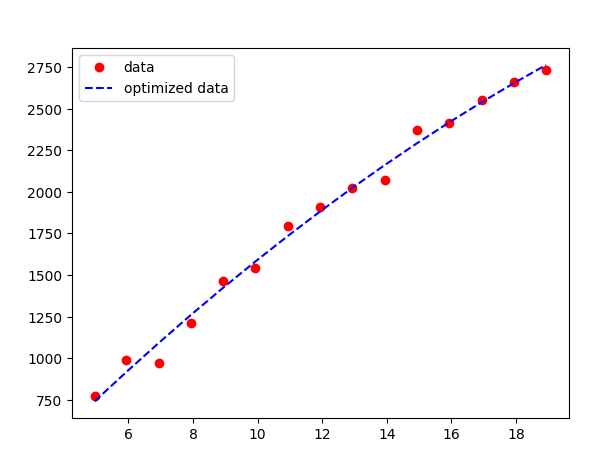
This is an example script which reads simulation results from play-results.json, then does curve fitting. It uses polynominal of the form a x ** 2 + b x + c, you can change the model. Then it plots model predictions composed with simulation results on the same plot.
The true model is a t ** 2 + b t + c, where t is log2 of number of nodes. This makes the problem more linear in my opinion. You can of course change that.
The example of the inverse function also provided - elo_to_nodes. I used it to test the model.