Note
asyncmachine-go is a declarative control flow library implementing AOP and Actor Model through a clock-based state machine.
aRPC is a transparent RPC for state machines implemented using asyncmachine-go. It's
clock-based and features many optimizations, e.g. having most of the API methods executed locally (as state changes are
regularly pushed to the client). It's built on top of cenkalti/rpc2, net/rpc,
and soheilhy/cmux. Check out a dedicated example, gRPC benchmark,
and integration tests tutorial.
- mutation methods
- wait methods
- clock pushes (from worker-side mutations)
- remote contexts
- multiplexing
- reconnect / fail-safety
- worker sending payloads to the client
- initial optimizations
Not implemented (yet):
WhenArgs,Err()PushAllTicks- chunked payloads
- TLS
- compression
- msgpack encoding
Each RPC server can handle 1 RPC client at a time, but 1 state source (asyncmachine) can have many RPC servers attached to itself (via Tracer API). Additionally, remote RPC workers can also have RPC servers attached to themselves, creating a tree structure (see /examples/benchmark_state_source).
Any state machine can be exposed as an RPC worker, as long as it implements /pkg/rpc/states/WorkerStructDef.
This can be done either manually, or by using state helpers (StructMerge,
SAdd), or by generating a states file with
am-gen. It's also required to have the states verified by Machine.VerifyStates.
Worker can send data to the client via the SendPayload state.
import (
am "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/machine"
arpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc"
ssrpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc/states"
)
// ...
// inherit from RPC worker
ssStruct := am.StructMerge(ssrpc.WorkerStruct, am.Struct{
"Foo": {Require: am.S{"Bar"}},
"Bar": {},
})
ssNames := am.SAdd(ssrpc.WorkerStates.Names(), am.S{"Foo", "Bar"})
// init
worker := am.New(ctx, ssStruct, nil)
worker.VerifyStates(ssNames)
// ...
// send data to the client
worker.Add1(ssrpc.WorkerStates.SendPayload, arpc.Pass(&arpc.A{
Name: "mypayload",
Payload: &arpc.ArgsPayload{
Name: "mypayload",
Source: "worker1",
Data: []byte{1,2,3},
},
}))Each RPC server can handle 1 client at a time. Both client and server need the same worker states definition (structure map and ordered list of states). After the initial handshake, server will be pushing local state changes every PushInterval, while state changes made by an RPC client are delivered synchronously. Server starts listening on either Addr, Listener, or Conn. Basic ACL is possible via AllowId.
import (
amhelp "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/helpers"
am "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/machine"
arpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc"
ssrpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc/states"
)
// ...
var addr string
var worker *am.Machine
// init
s, err := arpc.NewServer(ctx, addr, worker.ID, worker, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// start
s.Start()
err = amhelp.WaitForAll(ctx, 2*time.Second,
s.Mach.When1(ssrpc.ServerStates.RpcReady, ctx))
if ctx.Err() != nil {
return
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
// react to the client
<-worker.When1("Foo", nil)
print("Client added Foo")
worker.Add1("Bar", nil)Each RPC client can connect to 1 server and needs to know worker's states structure and order. Data send by a worker via
SendPayload will be received by a Consumer machine
(passed via ClientOpts.Consumer) as an Add
mutation of the WorkerPayload state (see a detailed diagram). Client supports
fail-safety for both connection (eg ConnRetries,
ConnRetryBackoff) and calls (eg CallRetries,
CallRetryBackoff).
After the client's Ready state becomes active, it exposes a remote worker at client.Worker. Remote worker implements
most of Machine's methods, many of which
are evaluated locally (like Is, When,
NewStateCtx). See machine.Api
for a full list.
import (
amhelp "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/helpers"
am "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/machine"
arpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc"
ssrpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc/states"
)
// ...
var addr string
// worker state structure
var ssStruct am.Struct
// worker state names
var ssNames am.S
// consumer
consumer := am.New(ctx, ssrpc.ConsumerStruct, nil)
// init
c, err := arpc.NewClient(ctx, addr, "clientid", ssStruct, ssNames, &arpc.ClientOpts{
Consumer: consumer,
})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// start
c.Start()
err := amhelp.WaitForAll(ctx, 2*time.Second,
c.Mach.When1(ssrpc.ClientStates.Ready, ctx))
if ctx.Err() != nil {
return
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
// use the remote worker
c.Worker.Add1("Foo", nil)
<-c.Worker.When1("Bar", nil)
print("Server added Bar")Because 1 server can serve only 1 client (for simplicity), it's often required to use a port multiplexer. It's very simple to create one using NewMux and a callback function, which returns a new server instance.
import (
amhelp "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/helpers"
arpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc"
ssrpc "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/rpc/states"
)
// ...
// new server per each new client (optional)
var newServer arpc.MuxNewServer = func(num int64, _ net.Conn) (*Server, error) {
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", t.Name(), num)
s, err := NewServer(ctx, "", name, w, nil)
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}
return s, nil
}
// start cmux
mux, err := arpc.NewMux(ctx, t.Name(), newServer, nil)
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}
mux.Listener = listener // or mux.Addr := ":1234"
mux.Start()
err := amhelp.WaitForAll(ctx, 2*time.Second,
mux.Mach.When1(ssrpc.MuxStates.Ready, ctx))
if ctx.Err() != nil {
return
}
if err != nil {
return err
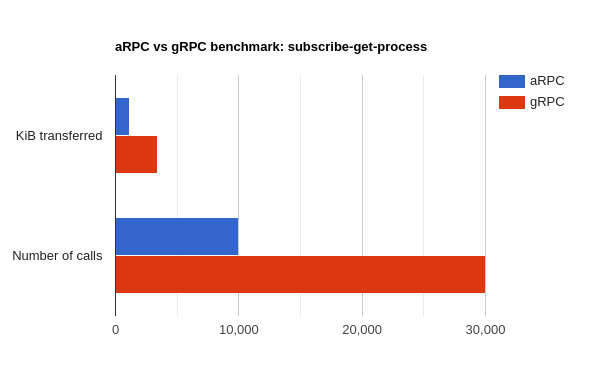
}A simple and opinionated benchmark showing a subscribe-get-process scenario, implemented in both gRPC and aRPC. See
/examples/benchmark_grpc for details and source code.
> task benchmark-grpc
...
BenchmarkClientArpc
client_arpc_test.go:136: Transferred: 609 bytes
client_arpc_test.go:137: Calls: 4
client_arpc_test.go:138: Errors: 0
client_arpc_test.go:136: Transferred: 1,149,424 bytes
client_arpc_test.go:137: Calls: 10,003
client_arpc_test.go:138: Errors: 0
BenchmarkClientArpc-8 10000 248913 ns/op 28405 B/op 766 allocs/op
BenchmarkClientGrpc
client_grpc_test.go:117: Transferred: 1,113 bytes
client_grpc_test.go:118: Calls: 9
client_grpc_test.go:119: Errors: 0
client_grpc_test.go:117: Transferred: 3,400,812 bytes
client_grpc_test.go:118: Calls: 30,006
client_grpc_test.go:119: Errors: 0
BenchmarkClientGrpc-8 10000 262693 ns/op 19593 B/op 391 allocs/op
BenchmarkClientLocal
BenchmarkClientLocal-8 10000 434.4 ns/op 16 B/op 1 allocs/op
PASS
ok github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/examples/benchmark_grpc 5.187s
aRPC implements /pkg/machine#Api, which is a large subset of /pkg/machine#Machine methods. Below the full list,
with distinction which methods happen where (locally or on remote).
// Api is a subset of Machine for alternative implementations.
type Api interface {
// ///// REMOTE
// Mutations (remote)
Add1(state string, args A) Result
Add(states S, args A) Result
Remove1(state string, args A) Result
Remove(states S, args A) Result
Set(states S, args A) Result
AddErr(err error, args A) Result
AddErrState(state string, err error, args A) Result
EvAdd1(event *Event, state string, args A) Result
EvAdd(event *Event, states S, args A) Result
EvRemove1(event *Event, state string, args A) Result
EvRemove(event *Event, states S, args A) Result
EvAddErr(event *Event, err error, args A) Result
EvAddErrState(event *Event, state string, err error, args A) Result
// Waiting (remote)
WhenArgs(state string, args A, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
// Getters (remote)
Err() error
// ///// LOCAL
// Checking (local)
IsErr() bool
Is(states S) bool
Is1(state string) bool
Not(states S) bool
Not1(state string) bool
Any(states ...S) bool
Any1(state ...string) bool
Has(states S) bool
Has1(state string) bool
IsTime(time Time, states S) bool
IsClock(clock Clock) bool
// Waiting (local)
When(states S, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
When1(state string, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenNot(states S, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenNot1(state string, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTime(
states S, times Time, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTicks(state string, ticks int, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTicksEq(state string, tick uint64, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenErr(ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
// Getters (local)
StateNames() S
ActiveStates() S
Tick(state string) uint64
Clock(states S) Clock
Time(states S) Time
TimeSum(states S) uint64
NewStateCtx(state string) context.Context
Export() *Serialized
GetStruct() Struct
Switch(groups ...S) string
// Misc (local)
Log(msg string, args ...any)
Id() string
ParentId() string
Tags() []string
SetLogId(val bool)
GetLogId() bool
SetLogger(logger Logger)
SetLogLevel(lvl LogLevel)
SetLoggerEmpty(lvl LogLevel)
SetLoggerSimple(logf func(format string, args ...any), level LogLevel)
Ctx() context.Context
String() string
StringAll() string
Inspect(states S) string
Index(state string) int
BindHandlers(handlers any) error
DetachHandlers(handlers any) error
StatesVerified() bool
Tracers() []Tracer
DetachTracer(tracer Tracer) bool
BindTracer(tracer Tracer) error
Dispose()
WhenDisposed() <-chan struct{}
IsDisposed() bool
}aRPC passes the whole test suite of /pkg/machine
for the exposed methods and provides a couple of optimization-focused tests (on top of tests for
basic RPC).
aRPC implements several optimization strategies to achieve the results.
net/rpcmethod names as runes- binary format of
encoding/gob - index-based clock
[0, 100, 0, 120]
- diff-based clock updates
[0, 1, 0, 1]
- debounced server-mutation clock pushes
[0, 5, 2, 1]
- partial clock updates
[[1, 1], [3, 1]]
Testing, not semantically versioned.
Go back to the monorepo root to continue reading.