LangChain provides tools and abstractions to simplify the development of applications powered by Large Language Models (LLMs).
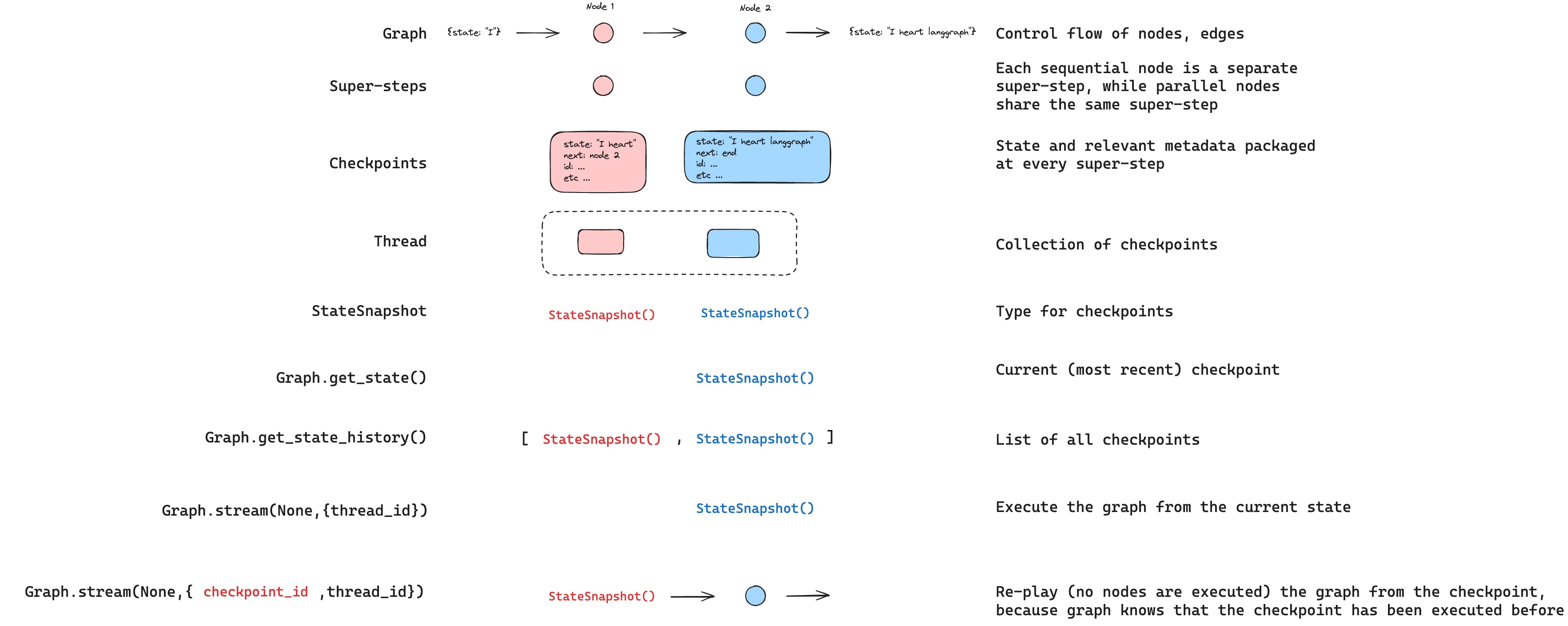
LangGraph introduces graph-based computation, enabling flexible and structured control flow for agents. Key concepts are:
-
Nodes: define specific computational unit or function within the graph.
-
Edges: determine the execution flow between nodes.
-
State: captures the intermediate and final results within the graph's execution.
-
Steps and Super steps: represent individual and grouped execution cycles, respectively.
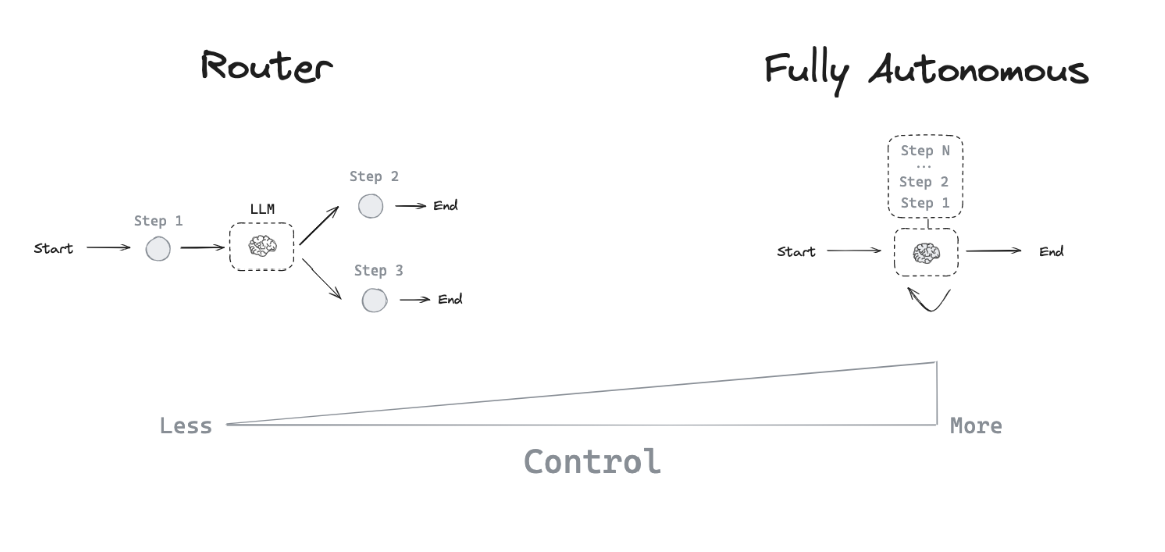
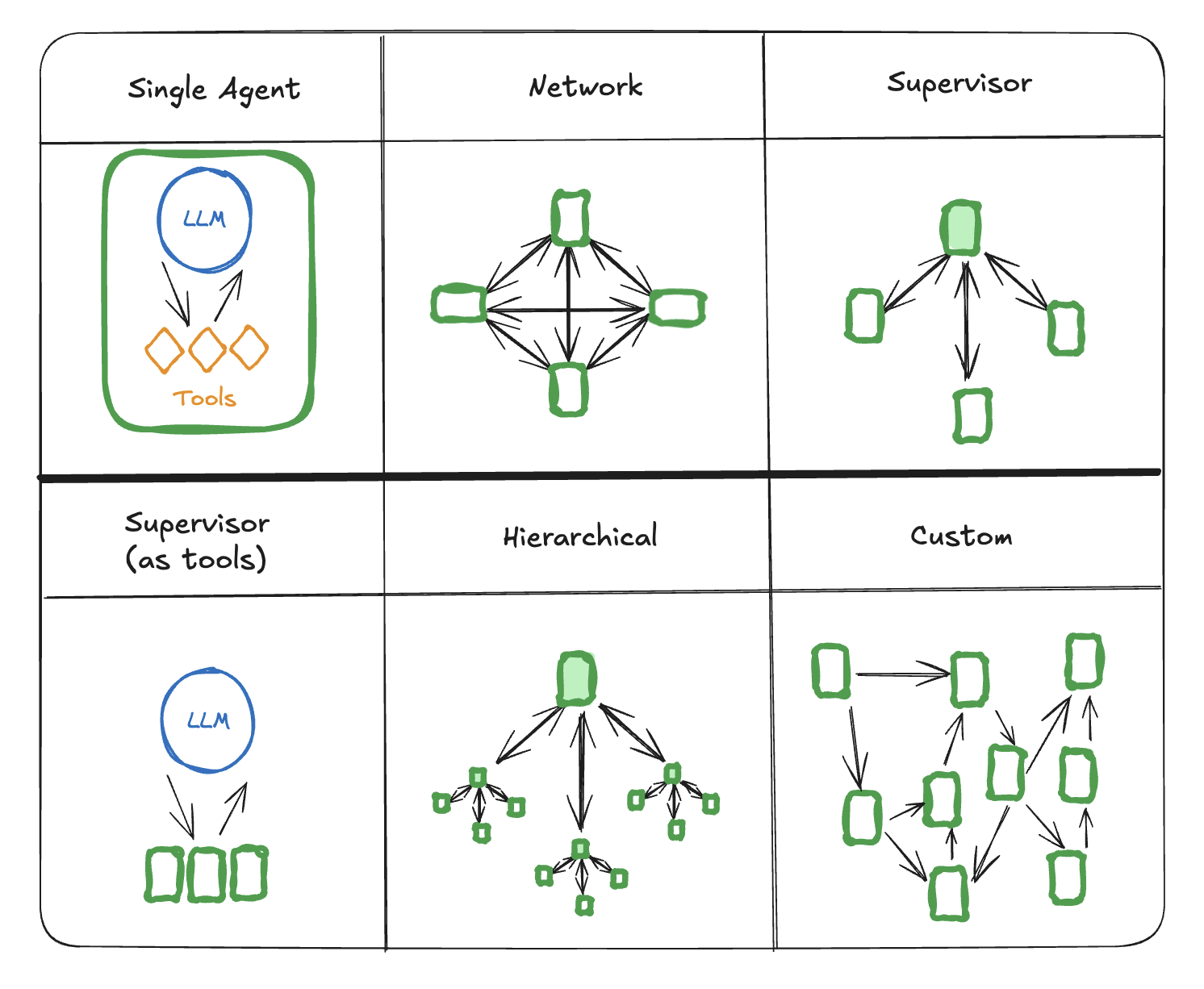
An Agent uses an LLM to dynamically decide its next actions and control flow based on inputs.
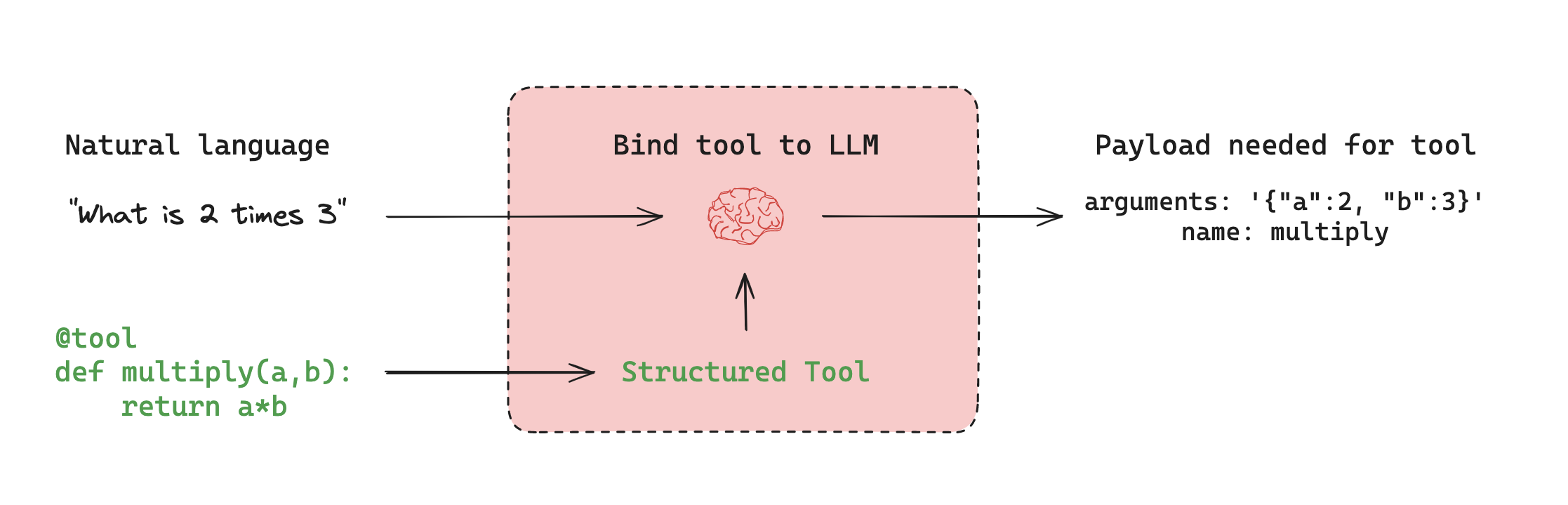
Agents can call tools and produce structured output:
from langchain.agents import Tool
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
def search_tool(query: str) -> str:
return f"Results for {query}"
llm = ChatOpenAI()
tools = [Tool(name="Search", func=search_tool, description="Searches the web")]
agent = create_react_agent(llm=llm, tools=tools)Save snapshots of graph states at specific steps:
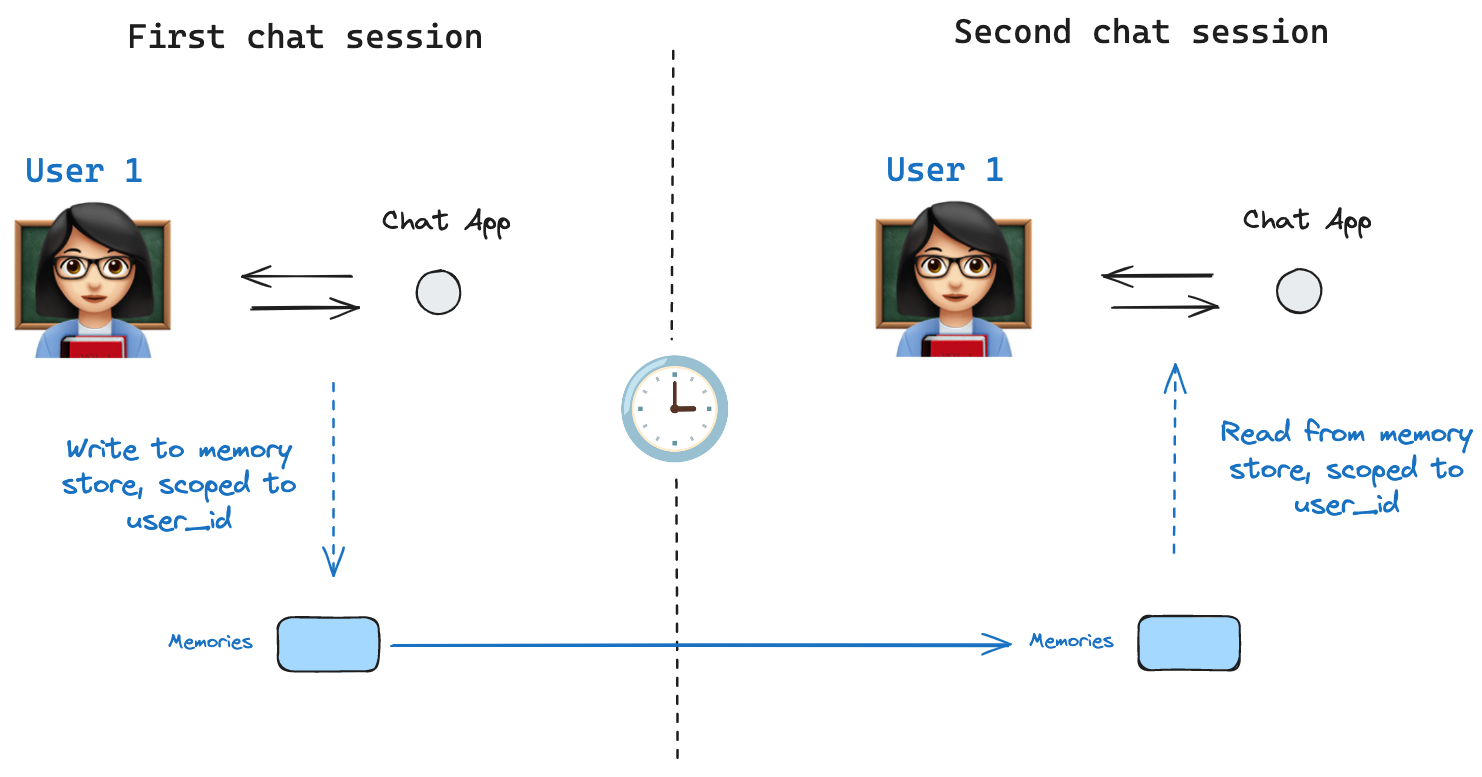
builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)Shared states enable persistent graph operations across runs.
-
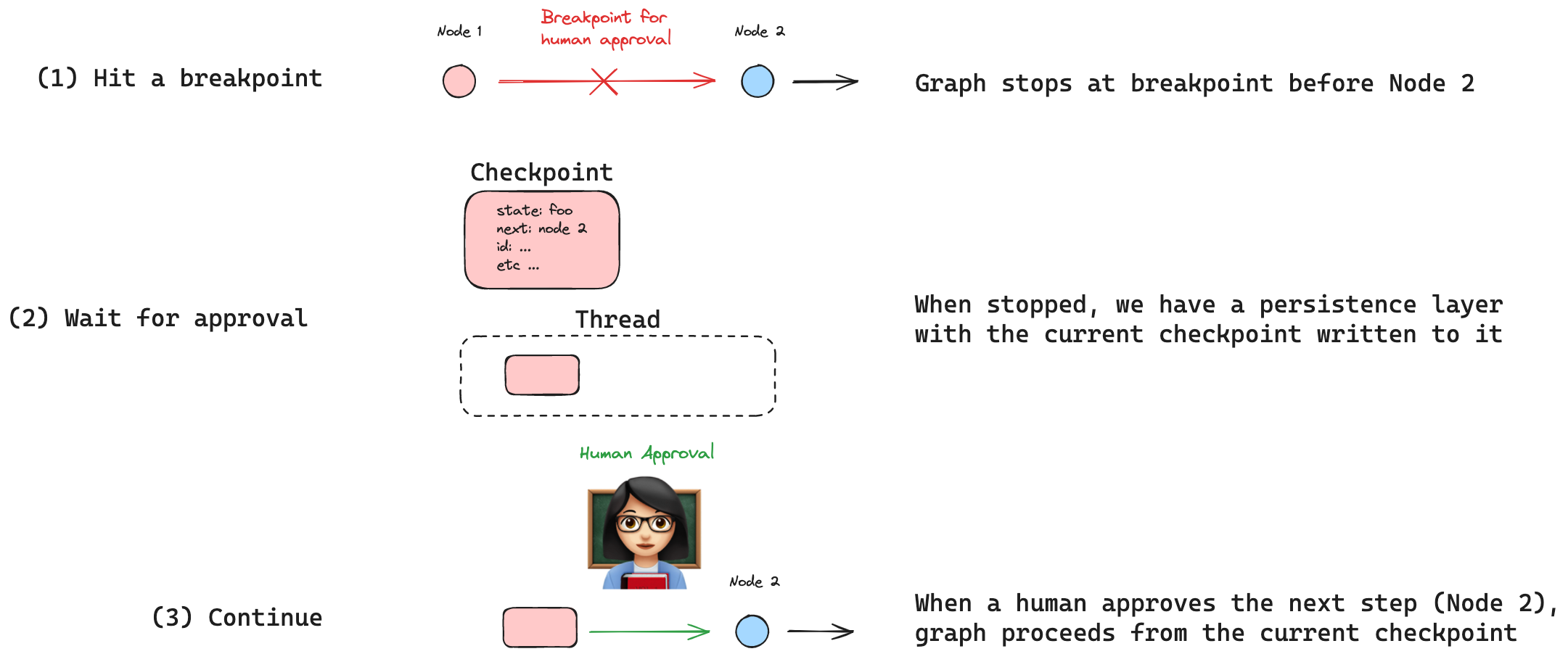
Approval: Pause for approval before proceeding.
-
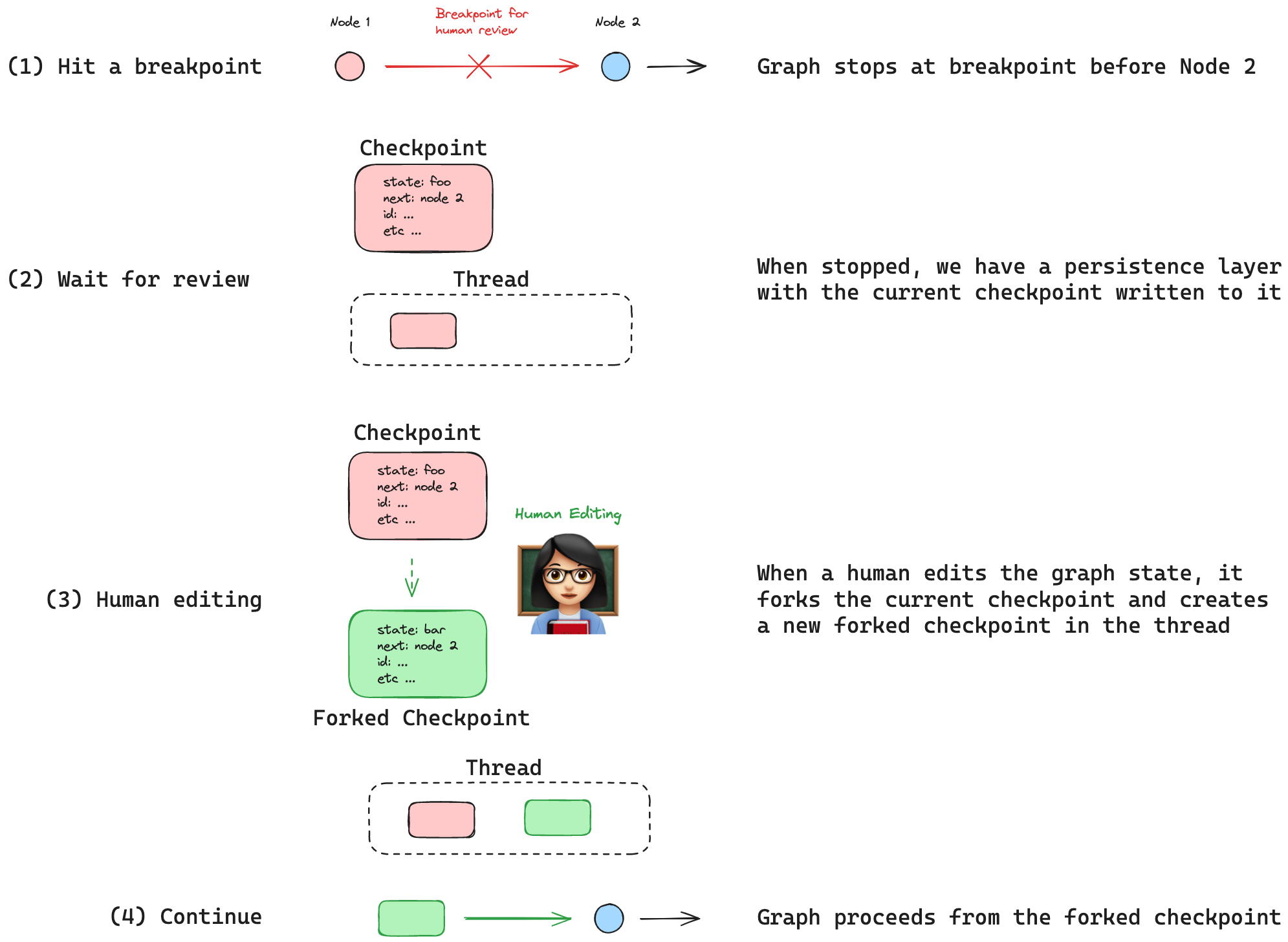
Editing: Allow manual changes to graph states.
-
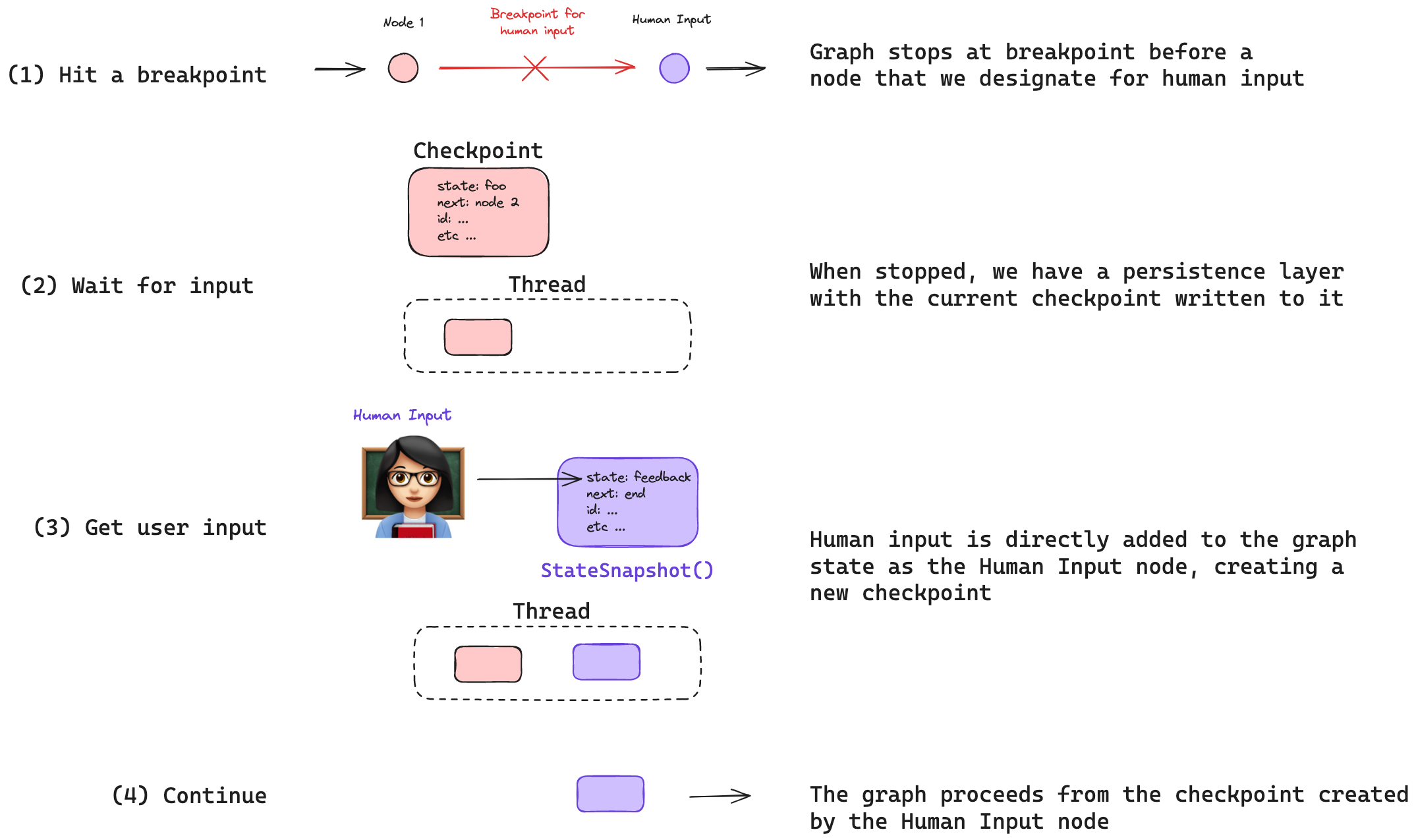
Input: Wait for explicit user input during execution.
Breakpoints enable stopping and resuming execution with human intervention.
# Define Breakpoint and State Interrupts
from langgraph.checkpoints import NodeInterrupt
def my_node(state: State) -> State:
if len(state['input']) > 5:
raise NodeInterrupt("Input too long")
return state
# Update state to bypass interruption
builder.compile().update_state(config=config, values={"input": "short input"})Debugging graphs involves tracing execution and inspecting state transitions.
Integrate tools like LangSmith and LangFuse for monitoring and logging graph-based LLM applications.
Clone the repository and set up the environment:
git clone https://github.com/cris96spa/llm_agents.git
cd llm_agents
# If make is installed
make dev-sync
# If make is not installed
uv sync --cache-dir .uv_cache --all-extras --no-group build